Special Issue "Water sustainability at global, regional and national levels"
Guest editors:
- Prof. Natalia Frolova, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia
- Prof. Frank Winde, North-West University, South Africa
- Prof. Chansheng He, Western Michigan University, USA
- Prof. Liliana Zaharia, University of Bucharest, Romania
- Dr. Maria Kireeva, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia
Special Issue "Water sustainability at global, regional and national levels"
Water consumption has been evaluated for the basins of the rivers flowing into the Arctic seas of the Russian Federation and, separately, for the Arctic zone of Russia (AZR). Long-term dynamics of the major characteristics of water consumption are given for the period from the 1980s to 2017 along with data on its structure. The possible effect of the total water withdrawal and consumptive water use on river water inflow into the Arctic seas has been evaluated for the 1980s (a period of maximal anthropogenic load), for 2006–2017 and up to 2030. The volumes of water consumption in limits of AZR are relatively low. Moreover, the water withdrawal has dropped considerably compared with the situation in the 1980s, in particular, by about 30% in the Pechora, Lena river basins, and from the rivers of Murmansk oblast, and by 50% in the Northern Dvina, Yenisei, and Kolyma river basins. It has increased in the Nenets and Yamalo-Nenets AO because of the intense development of the local oil-and-gas complex. Nowadays, according to the authors’ estimates, 21.28 km3/year is being withdrawn in the drainage basins of RF Arctic seas and 2.58 km3/year, within the AZR, or 28.8 and 3.5% of the total volume in Russia. The largest contribution to this value is due to the water-management complexes in the basins of the Ob (14.7 km3/year), Yenisei (2.77), Northern Dvina (0.64), and Murmansk oblast (1.72 km3/year). The volumes of water discharges back into water bodies at the drainage basins of Russian Arctic seas are comparable with the volumes of freshwater withdrawal -71% of water intake. Even lesser is the difference within AZR. The major water users are the industry (with a high proportion of mining plants), thermal power engineering, and municipal economy. But considerable and diverse hydrological restrictions exist at the municipal level and for some water users in AZR. These local hydrological restrictions have been formulated and analyzed in detail, for the first time. They form three large groups. Original maps are given to illustrate the specific features and regularities in the present-day distribution of water-management characteristics over AZR.
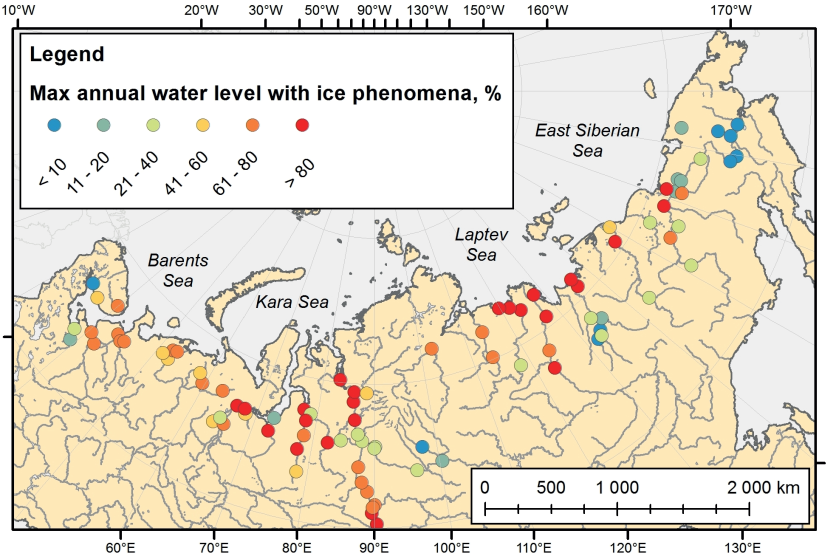
The ice regime of the Russian Arctic rivers and its hazardous manifestations under current climate conditions are characterized. The ice phenomena in rivers in the region determine the conditions of navigation, water supply, hydropower station (HPS) operation, and the construction of temporary ice bridges and roads. Data of more than 100 hydrological gages over period from 1936 to 2016 were used to compile various cartographic materials and to analyze the spatial variations of the dates of ice phenomena, the duration of ice-free and ice cover periods, and the maximal ice thickness. Special attention is paid to the characteristics of level regime in periods with ice phenomena. Data on the frequency of floodplain inundation during spring ice run, the hazard of ice jams, and the seasonal features of the passage of maximal annual water level are generalized.
The observed changes in ice regime characteristics and ice hazard are analyzed. The years of the start of statistically significant shift of the periods of ice phenomena, caused by both climate changes and anthropogenic impact, are identified. The increase in the duration of the ice-free period was found to be not greater than 3–4 days for East Siberian rivers, 5–6 days for the Middle and West Siberian rivers, and up to 10–12 days for the rivers in the European part. A decrease in the maximal ice thickness is most pronounced in the rivers of the Northern European Russia, where it is 10–15 cm. The frequency of floodplain inundation during spring ice run remains constant.
REGULAR ISSUE
ISSN 2542-1565 (Online)